What Is The Definition Of Quark Matter
In this definition there is a critical pressure and an associated critical density and when nuclear matter made of protons and neutrons is compressed beyond this density the protons and neutrons dissociate into quarks yielding quark matter probably strange matter. The antiparticle of a quark is the antiquark.
 What Is Antimatter Weak Interaction Quantum Chromodynamics Quantum Mechanics
What Is Antimatter Weak Interaction Quantum Chromodynamics Quantum Mechanics
Quarks are the particles that make up hadrons such as protons and neutrons.

What is the definition of quark matter. A state of matter which may exist at extremely high temperatures and densities composed of quarks and gluons moving freely and not bound together within hadrons. Quark matter is a type of ultra-dense matter which might be present in the cores of massive neutron stars. Quarks are the most basic known constituent of matter.
Any of a set of six hypothetical elementary particles together with their antiparticles thought to be fundamental units of all baryons and mesons but unable to exist in isolation. Quarks A class of fermion. However they cannot have an independent existence like protons or neutrons.
All matter except dark matter is made of molecules which are themselves made of atoms. An obvious but heuristic definition of quark matter is that it is matter which is built out of quarks. There are six different flavors or types of quark.
Is quark matter a sharply distinct phase of matter from nuclear matter. Quarks are the second group of fundamental particles leptons are the first. These particles make up the matter that we observe in our universe.
A quark k w ɔːr k k w ɑːr k is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matterQuarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons the most stable of which are protons and neutrons the components of atomic nuclei. These are the smallest building blocks of matter. Up quark down quark top quark bottom quark charm quark and strange quark.
The transition to quark matter has been estimated to occur at densities as low as 2 to 4 10 15 gcm 3 at zero temperature and at even lower densities at high temperatures. The atoms consist of two parts. They join to form hadrons such as protons and neutrons which are components of the nuclei of atoms.
Twelve fundamental particles - six quarks and six leptons the other type - are the basic building blocks for everything in the universe. Owing to a phenomenon known as color confinement quarks. As per quark physics definition it is the fundamental most particles present inside matter.
Quarks kwahrks kwawrks In physics the elementary particles that make up the protons and neutrons that in turn make up the atomic nucleus. Therefore two or more quarks combine to form a composite particle called hadrons. Quark any member of a group of elementary subatomic particles that interact by means of the strong force and are believed to be among the fundamental constituents of matter.
These quarks combine to produce composite particles called hadrons the most stable of which are neutrons and protons that are the components of atomic nuclei. The study of quarks and the interactions between them through the strong force is called particle physics. Quark definition is - any of several elementary particles that are postulated to come in pairs as in the up and down varieties of similar mass with one member having a charge of 23 and the other a charge of 13 and are held to make up hadrons.
Such a state of dense matter is called quark matter. All commonly observable matter is composed of up quarks down quarks and electrons. Or to put it another way.
Any of a group of elementary particles supposed to be the fundamental units that combine to make up the subatomic particles known as hadrons baryons such as neutrons and protons and mesons. The third and perhaps final group of fundamental particles is the carrier particles for the four basic forces. A quark is one of two currently recognized groups of fundamental particles which are subatomic indivisible at least as far as we know today particles that represent the smallest known units of matter.
The magnitude of their charge is either two thirds or one third of that of the electron. Proton is a stable hadron which comprises one down quark and two up quarks. Quark matter may have existed shortly after the Big Bang may exist in the cores of neutron stars and may be produced by the collision of two atomic nuclei at extremely high energy.
A quark is one of the fundamental particles in physics. A hypothetical highly energized form of matter that contains unbound quarks and gluons believed to have been present ten millionths of a second after the Big Bang. Is there a more precise definition.
The narrower meaning is quark matter that is more stable than nuclear matter. Leptons quarks and carrier particles may be all there is. Quark is a fundamental constituent of matter and is defined as an elementary particle.
 Quark Matter 2018 13 19 May 2018 Indico
Quark Matter 2018 13 19 May 2018 Indico
 Dew Drop To Quark Basic Physics Elementary Particle Physics
Dew Drop To Quark Basic Physics Elementary Particle Physics
 Quark Matter 2019 The Xxviiith International Conference On Ultra Relativistic Nucleus Nucleus Collisions 3 9 November 2019 Indico
Quark Matter 2019 The Xxviiith International Conference On Ultra Relativistic Nucleus Nucleus Collisions 3 9 November 2019 Indico
 Pion Definition Of Pion By Merriam Webster Commonly Misspelled Words Misspelled Words Rhyming Dictionary
Pion Definition Of Pion By Merriam Webster Commonly Misspelled Words Misspelled Words Rhyming Dictionary
 One Mind One Energy Com Physics Physics Laws Science
One Mind One Energy Com Physics Physics Laws Science
 Matter From Molecule To Quark For Example Of A Water Molecules Molecules Water Molecule Particles Of Matter
Matter From Molecule To Quark For Example Of A Water Molecules Molecules Water Molecule Particles Of Matter
 The Strange Insides Of Neutron Stars Berkeley Lab
The Strange Insides Of Neutron Stars Berkeley Lab
 Proof Of The Higgs Boson Is No Small Matter Postcard Zazzle Com Higgs Boson Quantum Mechanics Physics Teacher
Proof Of The Higgs Boson Is No Small Matter Postcard Zazzle Com Higgs Boson Quantum Mechanics Physics Teacher
 Quarks Theoretical Physics Quantum Foam Quantum Physics
Quarks Theoretical Physics Quantum Foam Quantum Physics
 At Last Physicists Understand Where Matter S Mass Comes From Elementary Particle Nuclear Physics Electron Configuration
At Last Physicists Understand Where Matter S Mass Comes From Elementary Particle Nuclear Physics Electron Configuration
 Quarks Are The Only Elementary Particles In The Physics To Experience All Four Fundamental Interactions Also Known As Fundament Physics Particles Star Citizen
Quarks Are The Only Elementary Particles In The Physics To Experience All Four Fundamental Interactions Also Known As Fundament Physics Particles Star Citizen
 Standard Model Mathematical Formulation Wikipedia Elementary Particle Physics Quantum Mechanics
Standard Model Mathematical Formulation Wikipedia Elementary Particle Physics Quantum Mechanics
 Standard Model Of Elementary Particles Standard Model Wikipedia Elementary Particle Physics Planck Length
Standard Model Of Elementary Particles Standard Model Wikipedia Elementary Particle Physics Planck Length
 Neutron Stars Tend To Lie In The Range Of 1 4 To 2 Solar Masses Any Star With A Neutron Star S Density That S Over 10 So Neutron Star Astronomy Universe Today
Neutron Stars Tend To Lie In The Range Of 1 4 To 2 Solar Masses Any Star With A Neutron Star S Density That S Over 10 So Neutron Star Astronomy Universe Today
 Quark Matter From Subquarks To The Universe Nova Science Publishers
Quark Matter From Subquarks To The Universe Nova Science Publishers
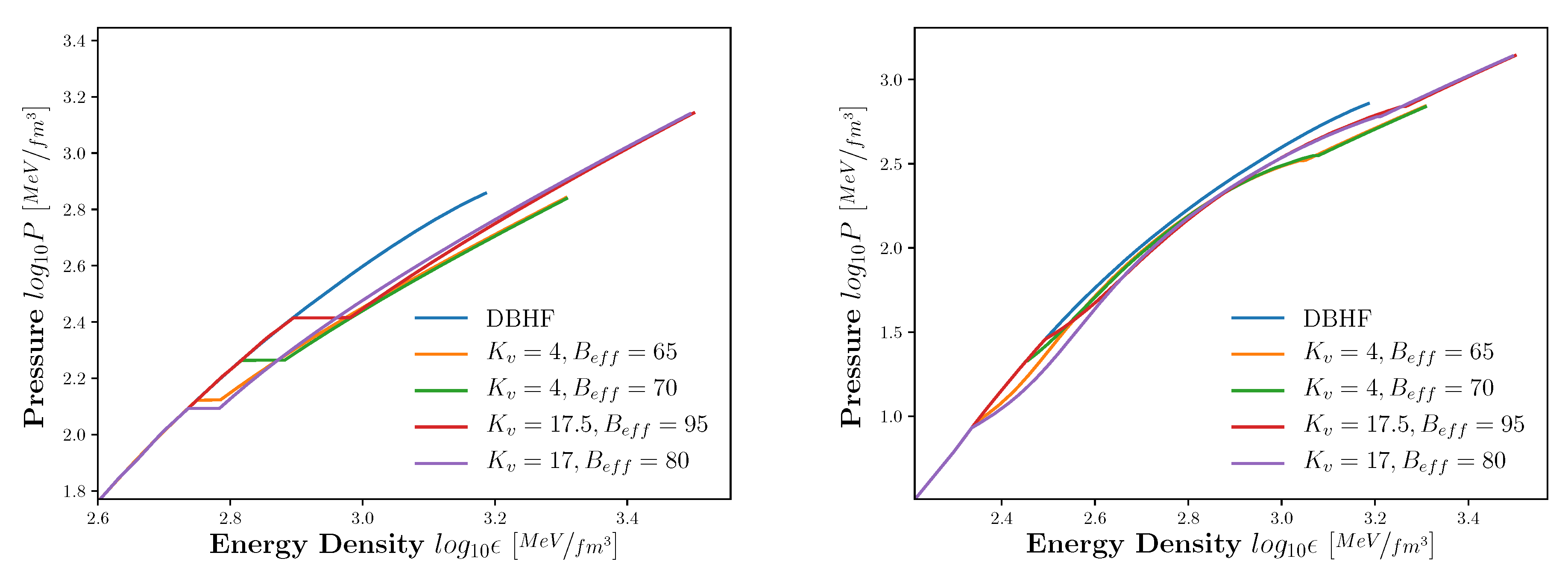 Universe Free Full Text Identifying Quark Matter In Hybrid Stars Through Relativistic Tidal Deformations Html
Universe Free Full Text Identifying Quark Matter In Hybrid Stars Through Relativistic Tidal Deformations Html


